A major energy transition is already underway, as the world races to meet the goals of the Paris climate agreement. But what will it mean for poorer communities? How can we ensure climate policy is fair? And what are the implications for investors?
The race is on
There is much political and financial capital devoted to tackling climate change in 2021. This reflects the growing realization by individuals, companies, investors and policymakers of just how crucial and urgent an issue climate is. We see this in politics: the new Biden administration’s green focus in the U.S., the further roll-out of Europe’s Green Deal, and China’s ambitious new climate goals. We see it too in investment practices — investors are increasingly allocating to green solutions, to both encourage the transition and to benefit from the growth opportunities it offers.
Global upheaval
There’s no denying that addressing climate change means shifting reliance on fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. The implications for the global economy are huge. It spells the end of fossil-fuel production. And there will have to be profound changes to supply chains in many sectors, particularly manufacturing and transport. The world will also have to create new green-energy production and distribution networks.
The price paid
This energy transition will bring substantial job opportunities in renewable energy research, extraction, distribution and corporate adaptation. But the global switch to clean fuels will also mean shutting down energy extraction plants around which entire communities and economies are built. The consequences of this shift for communities could be profoundly damaging if not managed the right way.
Well-intentioned and important policies to encourage the green transition risk hitting the poorest households hardest. For example, governments withdrawing fossil fuel subsidies is likely to drive up housing and transport prices. Wealthier households may switch to greener energy and electric cars, thanks to government incentive schemes. There will nevertheless be a cost to this switching that poorer households cannot afford.
This income disparity applies at country level too. Developed markets have benefited from fossil-fuel-led growth until now. Yet, emerging markets are expected to undertake the costly shift to renewable energy in order to comply with developed market demands. In particular, for emerging markets with fossil fuel resources, this is a significant sacrifice of potentially lucrative and inexpensive energy for populations already less well-off than their developed market counterparts.
These examples highlight how the unintended negative economic and social consequences of the energy transition would disproportionately affect more vulnerable households and societies at local, national and global level.
A fair transition
But all is not lost. Policymakers have the opportunity to act at every level to mitigate the economic and social hardships of the energy transition. Moreover, they can harness the transition to create opportunities for communities left behind by globalization, and damaged by the Covid-19 crisis.
Policymakers can harness the green transition to create opportunities for communities left behind by globalization, and damaged by the Covid-19 crisis.
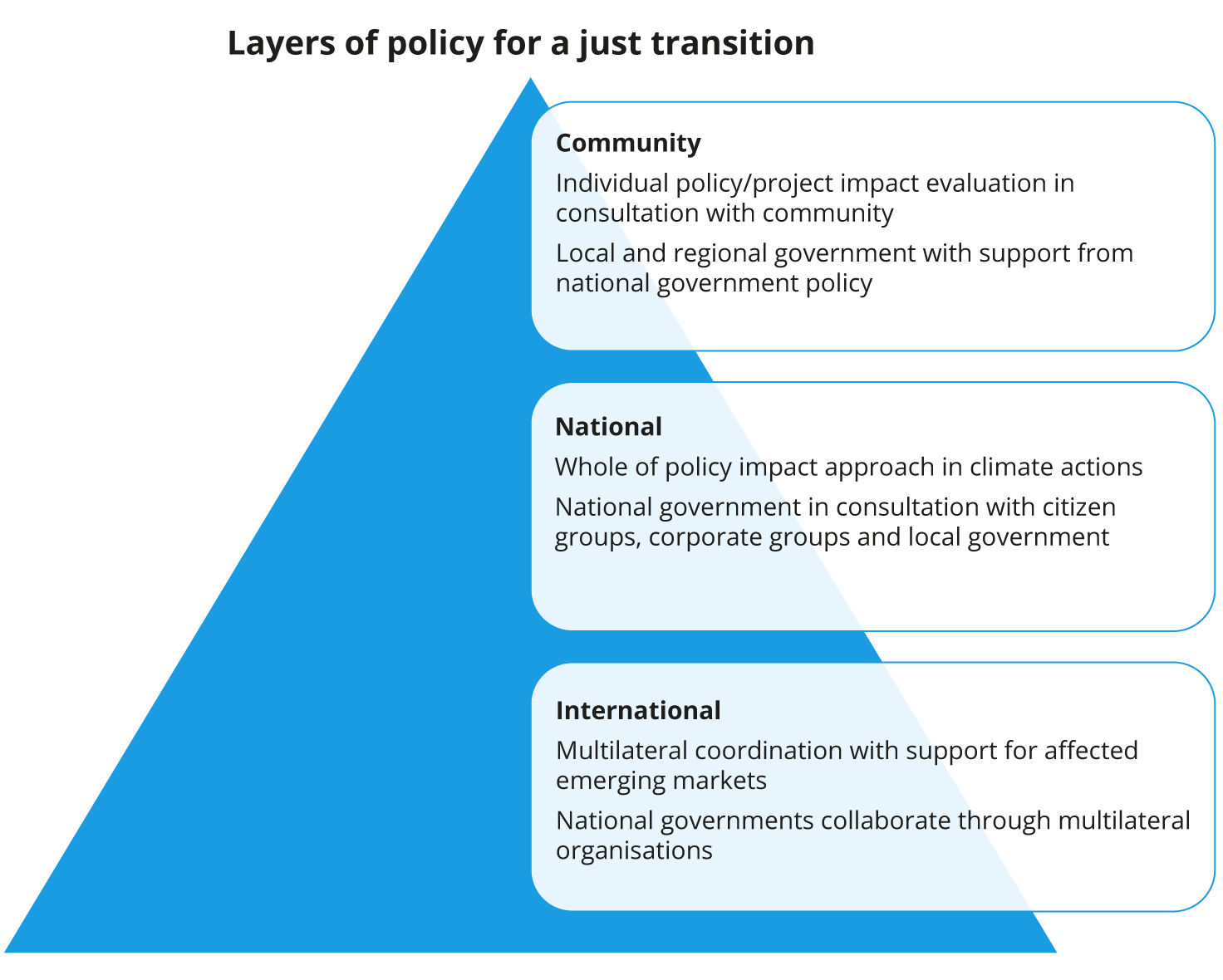
At local level, communities reliant on income and employment from carbon-intensive industry are at risk if production is shuttered because of the shift to green energy. These communities should be consulted early in the policy transition to ensure concerns are incorporated into policy solutions. Those solutions include re-skilling, social-welfare support, and strategies to create economic activity in affected communities. For example, green-energy production facilities could be sited where fossil fuel extraction once took place, to create alternative job opportunities.
Success at local level requires community collaboration and local government that understands the community challenges. It also requires central government support to draw upon when necessary, for social welfare, infrastructure investment funding and other ventures.
Central government also has a crucial role to play in setting national climate regulations, incentives and investments. The reality of the transition is that, through the period of change, people are at risk of losing their jobs. Communities could potentially suffer ‘brain drain’ if major employers are forced to close. There are two important messages for governments here. First, climate policy should incorporate a full economic impact analysis with corporate and citizen engagement. This will allow policymakers to fully understand the potential negative side effects from a given climate policy.
The second related message is that this is an environment that calls for smart government regulation and fiscal support. This means both minimizing the economic and social costs of the transition, while maximizing opportunities to create green jobs and infrastructure. By its nature, the energy transition will result in greater government spending, investment and regulation. Policy and regulation done well can provide a safety net and unlock opportunities for those at risk of being left behind.
What does it mean for investors?
For investors, this implies we can expect greater government intervention as a result of the climate change agenda. This is not a bad thing; it can be a sign governments are acting to reduce backlash to the transition and to improve long-term growth potential.
At global level, things get trickier. Developed market governments leading the charge on climate change must recognize the inequality it generates between advance and emerging economies. Investment and aid to affected emerging markets can help engender more global buy-in to climate solutions, and enable societies in the poorest regions to build industry around green technology.
None of these policies are simple to enact – particularly with regard to the emerging market versus developed market agenda. However, such policies are essential, not only to ensure a fair transition, but also to minimize the risks to the transition itself. The anti-globalization movement highlights the dangers of a rising tide that fails to lift all boats. Policymakers must not make the same mistakes with climate change. Time is not on our side.
This article was published in IFA Magazine and Wealth Magazine on March 19, 2021.
A just transition at every level
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Foreign securities are more volatile, harder to price and less liquid than U.S. securities. They are subject to different accounting and regulatory standards, and political and economic risks. These risks are enhanced in emerging markets countries.
US-220321-145515-1